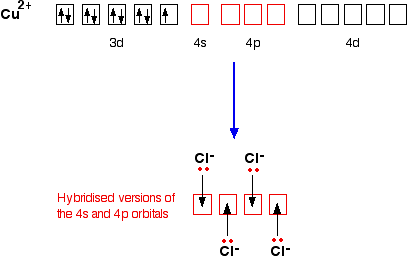
Copper Cu transition metal Chemistry copper(I) Cu+ copper(II) Cu2+ ion complex ions ligand substitution compounds redox chemical reactions principal oxidation states +1 +2 GCE AS A2 IB A level inorganic chemistry revision

Why is Cu+ diamagnetic while Cu2+ is paramagnetic? | by KAKALI GHOSH , Teacher,blogger. M.Sc chemistry. | Medium

Schematic presentation for Cu(II) ion removal mechanisms by nZVI particles | Download Scientific Diagram
![SOLVED: (12pts) Separation of Copper(II) and Bismuth(III) Ions Procedure Number and Ion Test Reagent or Technique Evidence of Chemical Change Chemical(s) Responsible for Observation [6] Cu2+ NH4OH Deep blue solution [ Cu(NH3)4]2+ [7] SOLVED: (12pts) Separation of Copper(II) and Bismuth(III) Ions Procedure Number and Ion Test Reagent or Technique Evidence of Chemical Change Chemical(s) Responsible for Observation [6] Cu2+ NH4OH Deep blue solution [ Cu(NH3)4]2+ [7]](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_previews/4282f638-d25f-422c-8f96-da4404930084_large.jpg)
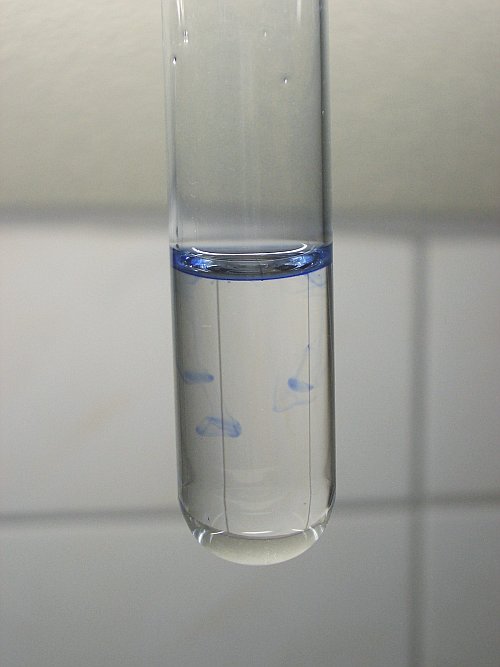
SOLVED: (12pts) Separation of Copper(II) and Bismuth(III) Ions Procedure Number and Ion Test Reagent or Technique Evidence of Chemical Change Chemical(s) Responsible for Observation [6] Cu2+ NH4OH Deep blue solution [ Cu(NH3)4]2+ [7]

Copper Cu transition metal Chemistry copper(I) Cu+ copper(II) Cu2+ ion complex ions ligand substitution compounds redox chemical reactions principal oxidation states +1 +2 GCE AS A2 IB A level inorganic chemistry revision

Ch 7.1 Forming Ions. Review… Cations are Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A They have positive charges. Anions are Groups 5A, 6A, and 7A They have negative charges. - ppt download